Microset can be used to measure ship’s chronometers. The picture below shows a Russian chronometer in its case. A MicroSet flat disk acoustic sensor is sitting on the glass face. A short length of brass rod is used to weight the disk down so it makes good acoustic contact. This arrangement captures the tick sound easily. The flat disk sensor is one of many accessories available for MicroSet.

In the MicroSet graph below, you can see several hours of rate from this chronometer. MicroSet was configured to take a reading every 60 ticks. The level control was set to trigger on the main tick of the chronometer with a period of 1/2 second, so a new reading is taken every 30 seconds. To insure reliable readings, the Blanking Window was engaged. This makes MicroSet “deaf” for most of the time, and only allows the timer to be triggered just as the next tick sound is expected.
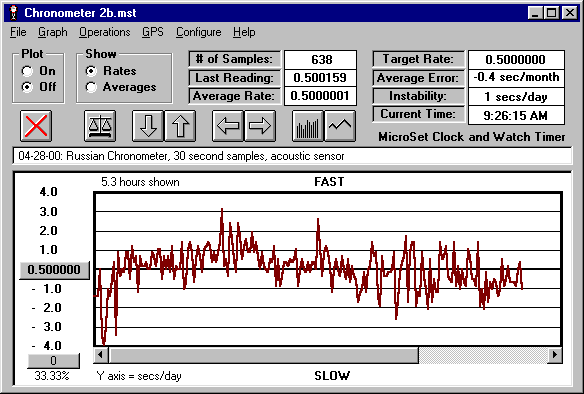
The graph shows us that this chronometer is running on time, though there is a gradual shifting of rate over the 5 hours of this sample. The range of this rate drift was approximately +/- three seconds per day. A longer study would help us determine the source of this variation and whether or not it is cumulative or self canceling. The Instability Factor is just one second per day, which measn the rate is quite stable.
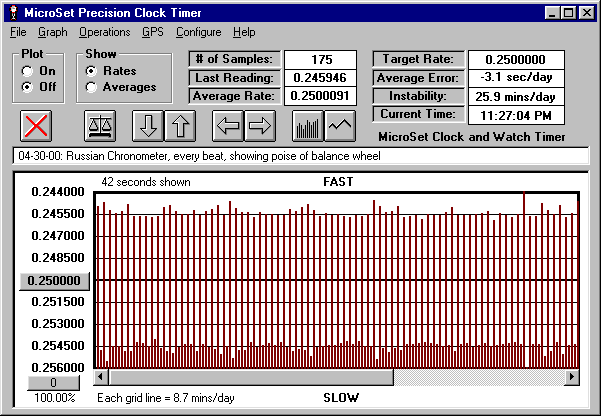
MicroSet 3 has the ability to measure every beat of a clock. (The previous versions of MicroSet skip a beat every time they report a reading.) By being able to measure every beat, you can see a very detailed view of the relationship between the even and odd beats of a chronometer balance wheel. The following graph shows such a reading. Note that every other beat is fast or slow of the correct rate of .250000 seconds. This tool will allow you to view these details of the balance wheel with a resolution to a millionth of a second.